Solar Energy Inverter:Choose the Best Inverter for Solar Power

Discover how a solar energy inverter works, how to choose the best one, and explore top tips to maximize your solar power efficiency with this complete guide.
When building a solar power system, one essential component that should not be overlooked is the solar energy inverter. This device plays a crucial role in converting the direct current (DC) electricity generated by your solar panels into usable alternating current (AC) power for your home or business.

Solar energy inverter
In this guide, we will delve in-depth into everything you need to know about solar inverters — what they are, how they work, the types available, how to choose the best solar inverter for your needs, and tips to maximize your solar power system. Whether you are considering residential solar panel installation or commercial solar power systems, understanding solar inverters will help you make the best decision.
What Is a Solar Energy Inverter and Why Is It Important?
A solar energy inverter is an electronic device that changes the DC electricity produced by solar panels into AC electricity, which powers household appliances and feeds energy into the electrical grid.
Without a solar inverter, the energy your solar panels create would not be usable in standard electrical systems, as electricity from the grid and most appliances run on AC.
The inverter also optimizes the solar system’s performance by:
- Tracking maximum power points to extract the highest possible energy from the panels
- Synchronizing with the grid for seamless power delivery
- Providing safety features such as automatic shutdowns during power outages
In other words, the right inverter ensures your solar power system is efficient, safe, and reliable.
Types of Solar Energy Inverters
Different types of solar inverters are designed to suit various system configurations and budgets:
1. String Inverters
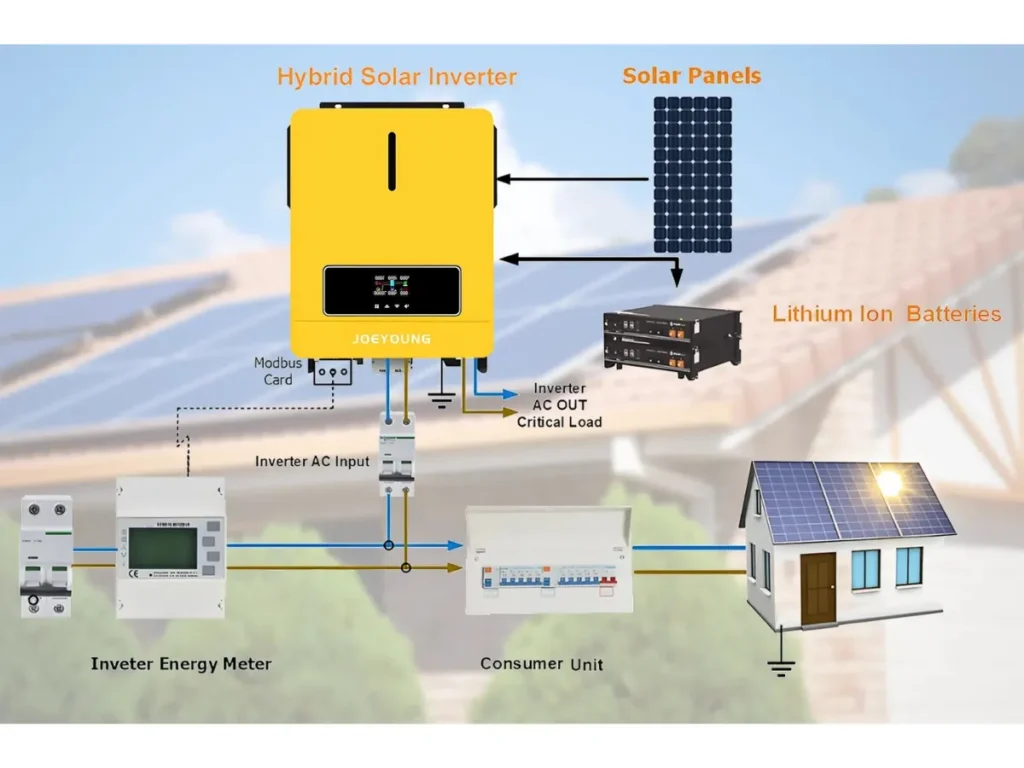
This is the most common type used in residential and commercial solar power systems. Multiple solar panels connect in series (a “string”), with their combined DC fed into a single inverter that converts it to AC.
Advantages:
- Cost-effective and widely available
- Easy to install and maintain
- Good for well-shaded or uniform panel setups
Considerations:
- If one panel’s output drops, it affects the entire string’s output
- Less energy optimization per panel
2. Microinverters
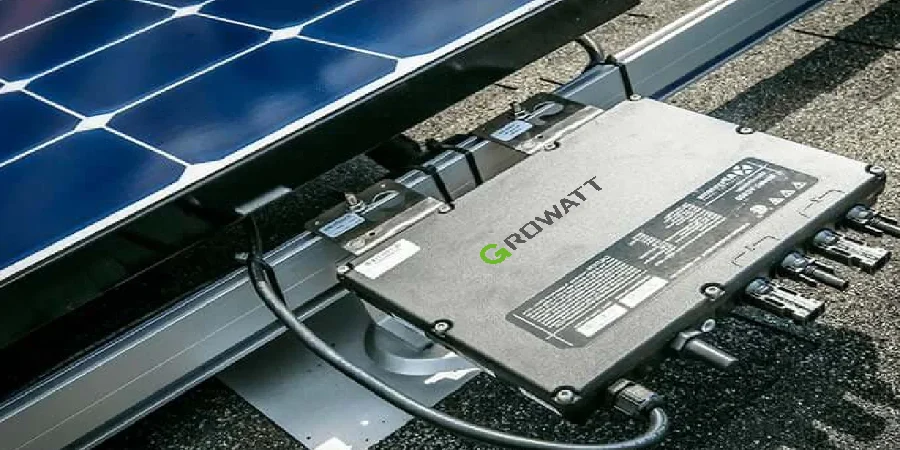

micro solar inverter
Microinverters are small inverters attached to each solar panel individually. They convert DC to AC right at the panel level.
Advantages:
- Maximizes the output of each panel, beneficial for shaded or varied orientation systems
- Easier to expand the system size later
- Better monitoring capabilities per panel
Considerations:
- Higher upfront cost
- Slightly more complex installation
3. Power Optimizers (with String Inverters)
Power optimizers work with string inverters but optimize each panel’s output before sending DC to the inverter.
Advantages:
- Combining the benefits of microinverters and string inverters
- Improved performance and shading tolerance
- Cost-effective alternative to microinverters
Considerations:
- Requires a compatible string inverter
- Slightly higher cost than standard string inverter
4. Hybrid Inverters
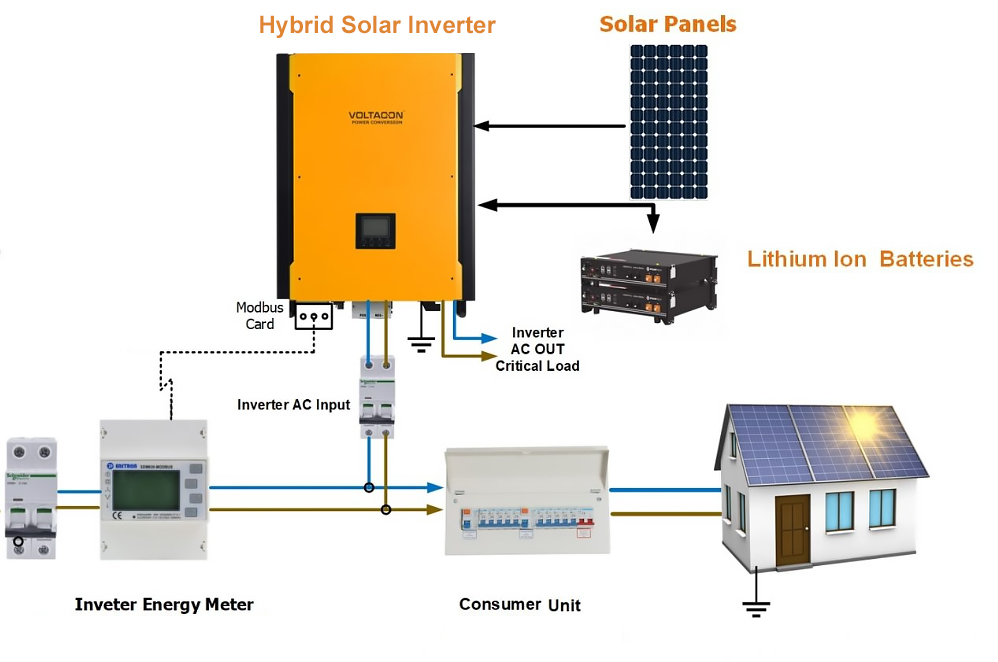
These inverters can operate with both solar panels and battery storage. They manage solar energy, store excess energy in batteries, and supply power when needed.
Advantages:
- Ideal for home solar battery storage systems
- Provides backup power during outages
- Simplifies system integration
Considerations:
- Higher cost than standard inverters
- More complex system design
String and Micro Inverter based on recent expert summaries and technical explanations:
| Feature | String Inverter | Microinverter |
|---|---|---|
| Basic Function | Converts DC electricity from a string (series) of solar panels into AC power in one central unit. | Converts DC power to AC at each solar panel separately. |
| Installation Location | Usually installed in a single location on the side of the house or shaded area. | Mounted under each solar panel on the roof. |
| Suitability | Best for simple, unshaded roofs with panels arranged in uniform strings. | Ideal for complex roof shapes, shading issues, or panels facing different directions. |
| Cost | Lower upfront cost; fewer components to install, easier for larger systems. | Higher upfront cost due to one inverter per panel, but may reduce long-term losses. |
| Performance Optimization | Limited to string-level optimization; output constrained by weakest panel in string. | Optimizes output per panel independently, reducing shading losses. |
| System Expandability | Adding more panels may require inverter upsizing or additional string inverters. | Easy to expand the system panel-by-panel without replacing the inverter. |
| Maintenance and Repairs | Centralized repairs are needed if the inverter fails; easier access, but downtime affects the whole system. | Easy to expand the system panel-by-panel without replacing the inverter. |
| Monitoring | Typically monitors at the string level, not the panel level. | Provides module-level monitoring with detailed performance data per panel. |
| Efficiency | Typically monitors at the string level, not the panel level. | Higher system efficiency in real-world shading or complex layouts due to individual panel optimization. |
| Lifespan | Usually lasts 10 to 15 years; replacement is likely during the solar panel’s lifespan. | Often has a longer warranty (around 25 years), matching panel life. |
| Space Requirements | Requires more physical space in the home for the single unit. | Minimal additional space needed on the roof, integrated under the panels. |
| Safety | Generally safe; located off the roof, reducing risk exposure. | Meets rapid shut-down and safety standards with panel-level control. |
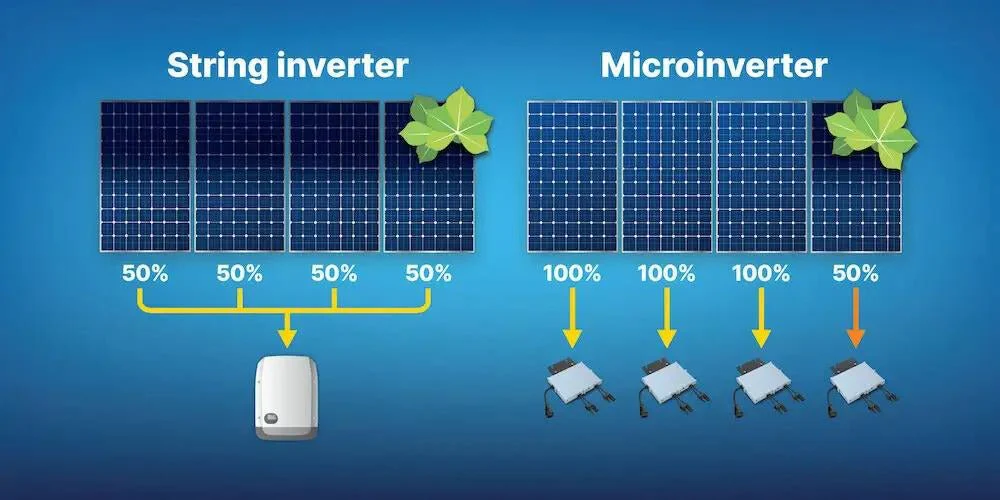
Summary:
- String inverters are cost-effective and reliable for larger, uncomplicated solar panel arrays in full sun. They require less initial investment and simpler maintenance, but suffer power loss if a single panel underperforms.
- Microinverters deliver better overall performance in environments where shading, complex roofs, or future expansion is expected. Despite higher upfront cost and more maintenance points, they offer superior monitoring and enhanced energy harvest per panel.
Choosing between them depends on your roof layout, shading conditions, budget, and preference for monitoring and expansion flexibility.
This overview is based on authoritative solar energy sources such as Growatt, EnergySage, SolarReviews, PSC Energy, and recent detailed guides from the solar industry.
How to Choose the Best Solar Energy Inverter for Your System
Selecting the right solar energy inverter depends on the following criteria:
1. System Size and Power Needs
Calculate the total wattage of your solar panel system. The inverter’s capacity should match or slightly exceed this to handle peak production efficiently.
2. Type of Solar Panel Setup
Consider your system layout. For uniform, unshaded arrays, string inverters work well. For partial shading or complex layouts, microinverters or power optimizers may be better.
3. Budget Constraints
String inverters usually cost less upfront. Microinverters or hybrid systems have higher initial prices but may offer better long-term performance.
4. Battery Compatibility
If you plan to add a solar battery storage system, consider hybrid inverters made to integrate with batteries.
5. Efficiency Ratings
Look for an inverter efficiency above 95% to minimize energy loss during conversion.
6. Warranty and Brand Reputation
Reputable brands often provide longer warranties (typically 10-15 years) and reliable customer support.
7. Monitoring and Smart Features
Many inverters offer remote monitoring via apps to track system performance in real-time.
8. Safety Certifications
Ensure compliance with standards and certifications relevant to your country or region, such as UL, IEC, or others.
Top Brands and Models of Solar Energy Inverters
Some of the leading solar inverter manufacturers recognized worldwide include:
- SolarEdge: Known for power optimizers combined with string inverters, enabling high efficiency.
- Enphase: A pioneer in microinverters, popular for residential applications.
- Fronius: Offers reliable string inverters with advanced features and monitoring.
- SMA: A global leader with a wide range of string and hybrid inverters.
- Huawei: Provides cost-effective string inverters with smart technology.
Choosing from these brands helps ensure you receive a quality inverter with good support.
Installation and Maintenance Tips for Solar Energy Inverters
- Always hire a licensed solar professional for system design and inverter installation to ensure safety and compliance.
- Install the inverter in a cool, shaded, and well-ventilated area to prevent overheating.
- Keep the inverter clean and dust-free. Regularly inspect for physical damage.
- Monitor system performance using the inverter’s monitoring platforms to detect issues early.
- Schedule periodic professional maintenance for long-term system health.
Advantages of Using a Solar Energy Inverter
- Converts solar power into usable household energy.
- Increases solar system efficiency with smart tracking.
- Enables integration with grid and battery storage systems.
- Supports energy independence and reduced electricity costs.
- Enhances system safety with automatic shut-off features.
Conclusion
A solar energy inverter is a central component that determines the efficiency, safety, and reliability of your solar power system. Choosing the right inverter involves understanding your system size, budget, layout, and plans like battery storage.
By selecting quality inverters from trusted brands and following best installation practices, you ensure long-lasting, high-performing solar energy systems that save money and reduce environmental impact.
Invest wisely in your solar inverter to fully use the power of the sun for years to come.
FAQs
What size solar inverter do I need?
Match the inverter size to the total wattage of your solar panels, typically allowing a 10-20% buffer to prevent overload.
Some systems allow inverter upgrades, but it’s best to plan the correct size and type initially.
Most inverters last 10-15 years, often backed by a warranty.
Yes, especially in shaded or partially shaded environments.
Can a solar inverter work without batteries?
