RV Solar Panel System Components: A Complete Guide for 2025
Learn about the essential components of an RV solar panel system, including panels, charge controllers, batteries, and inverters. Discover how each part works to power your RV off-grid
If you’re interested in harnessing solar power for your RV, understanding the key RV solar panel system components is essential. Each part plays a crucial role in capturing, storing, and using solar energy to keep your RV running smoothly on the road or while boondocking.
Introduction to RV solar panel components
In this guide, we explain the main components of an RV solar system, how they work together, and what you should know when choosing equipment for your solar setup. In 2025, trends in RV solar system components are focused on increased efficiency, smart integration, and lightweight designs. Key areas include higher-efficiency solar panels, integration with smart energy management systems, and the use of advanced battery technologies like Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4). Also, lightweight and flexible panels are becoming more popular for easier installation and portability.
Here’s a more detailed breakdown:
1. Increased Efficiency:
- High-efficiency solar cells: Manufacturers are developing panels that maximize power output from smaller footprints, crucial for space-constrained RVs.
- Monocrystalline vs. Polycrystalline vs. Thin-film: Monocrystalline panels are known for their higher efficiency, while thin-film panels are more flexible and suitable for curved RV roofs.
2. Smart Integration:
- Smart energy management systems: These systems allow RV owners to monitor energy consumption, optimize power usage, and potentially integrate with other smart home features.
- Integration with appliances:12V battery-powered appliances (like water heaters and air conditioning) are becoming more common, allowing for off-grid capabilities.
3. Lightweight and Flexible Designs:
- Flexible solar panels:These panels can conform to the shape of the RV roof, making them easier to install and potentially more aesthetically pleasing.
- Lightweight materials: Reducing the overall weight of the RV solar system improves fuel efficiency and overall performance.
4. Advanced Battery Technologies:
- Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) batteries: These batteries offer higher energy density, longer lifespan, and improved safety compared to traditional lead-acid batteries.
- Battery management systems (BMS): These systems help optimize battery performance, prevent overcharging and discharging, and extend battery life.
5. Other Notable Trends:
Sustainability: There’s a growing emphasis on eco-friendly features and sustainable practices in RV manufacturing and solar panel technology.
Portable and foldable panels: These offer greater flexibility for different camping locations and situations.
Hybrid systems: Combining solar power with other energy sources (like generators) can provide enhanced reliability.
What Are the Main Components of an RV Solar Panel System?
A typical RV solar system consists of the following key parts:
1. Solar Panels
Solar panels capture sunlight and convert it into direct current (DC) electricity. For RVs, panels are usually either rigid monocrystalline or polycrystalline, or flexible panels if roof space and aesthetics are a concern.
- Monocrystalline panels are efficient and perform well in a limited space.
- Polycrystalline panels are more affordable but a bit less efficient.
- Flexible panels are lightweight and can bend to fit curved RV roofs.
2. Charge Controller
The charge controller regulates the voltage and current coming from the solar panels to the battery bank. This prevents overcharging and prolongs battery life.
There are two main types:
- PWM (Pulse Width Modulation): A basic and cost-effective controller for small systems.
- MPPT (Maximum Power Point Tracking): More efficient, allowing solar panels to produce maximum power, and works well in larger or complex RV systems.
3. Battery Bank
Batteries store the electricity generated by the solar panels to power your RV appliances when sunlight isn’t available.
Common types used in RV solar systems include:
- Lead-Acid Batteries: Affordable but heavier, require maintenance, and have a shorter lifespan.
- Lithium-Ion Batteries: More expensive but lighter, longer-lasting, and require less maintenance.
4. Inverter
An inverter converts DC electricity stored in the batteries into alternating current (AC) electricity, which powers most household appliances in your RV.
- Pure Sine Wave Inverters provide clean power suitable for sensitive electronics.
- Modified Sine Wave Inverters are cheaper but less compatible with delicate devices.
5. Wiring and Connections
Good quality wiring and connectors ensure the efficient and safe flow of electricity between panels, controllers, batteries, the inverter, and the RV electrical system.
6. Mounting Hardware
Proper mounting equipment secures solar panels to your RV’s roof, ensuring stability and optimal angle for sun exposure.
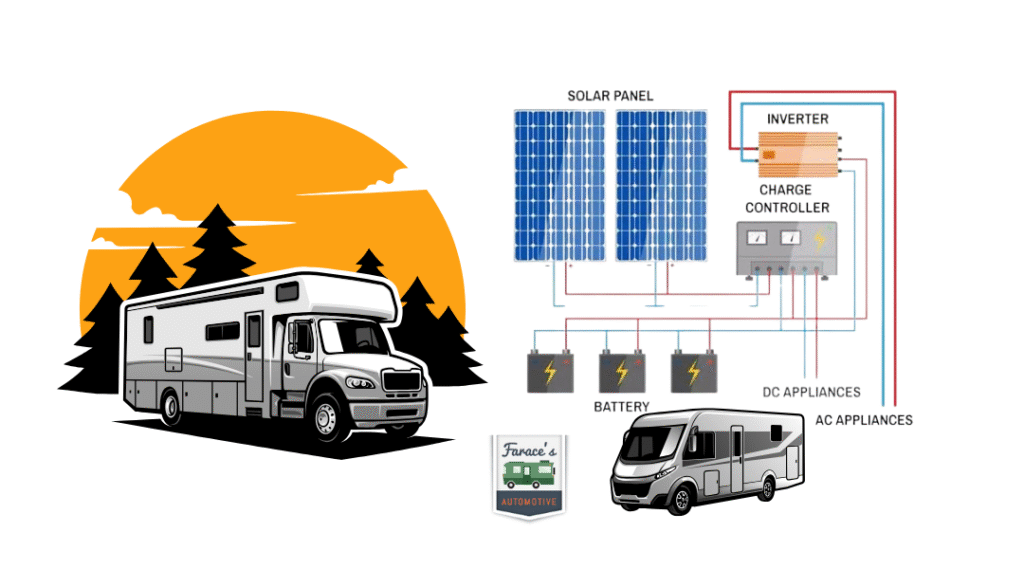
How These Components Work Together in an RV Solar System
Understanding how all the parts of an RV solar panel system interact is essential to appreciating the technology that powers your adventures off the grid. Each component plays a crucial role, working seamlessly together to capture sunlight, store energy, and deliver power to your RV appliances. Let’s break down this energy flow step-by-step:
1. Solar Panels Capture Sunlight and Generate Electricity
Solar panels on your RV’s roof absorb sunlight and convert it into direct current (DC) electricity through a process called the photovoltaic effect. The amount of DC electricity generated depends on the panel’s size, efficiency, sunlight intensity, and shading conditions.
You usually have several panels connected, either in series or parallel, to create the right voltage and current levels that your system needs.
2. Charge Controller Regulates Electricity Flow into Batteries
The electricity from the solar panels is sent to the charge controller, a key safety device that manages the charging process to protect your batteries.
The controller continuously monitors the battery’s state of charge and adjusts the voltage and current from the panels to maximize charging efficiency while preventing overcharging, which can damage batteries.
Modern charge controllers, especially MPPT types, optimize the power extracted from panels under varying weather conditions, making your system more efficient and allowing for longer battery life.
3. Batteries Store Energy for When the Sun Isn’t Shining
The charge controller sends the regulated DC power to your battery bank, where energy is stored chemically for later use, such as during nighttime or cloudy days.
The size and type of your battery bank determine how much energy you can store and how long you can power your RV off-grid without sunlight.
Batteries act as a buffer, smoothing out the intermittent nature of solar power so you have reliable electricity 24/7.
4. Inverter Converts Battery DC Power to AC Power for Appliances
Most RV appliances and electronics run on alternating current (AC) power, just like your home. Since your solar panels and batteries produce and store DC power, it needs to be converted to AC.
This is the job of the inverter — an electronic device that takes the DC electricity from your batteries and converts it into the familiar 120V AC (in the US) to run your lights, refrigerator, microwave, and devices.
Choosing a pure sine wave inverter ensures your power is clean and safe for sensitive electronics.
5. Wiring Connects All Components Safely and Efficiently
High-quality wiring and connectors interlink all the system parts, allowing a smooth, safe flow of electricity with minimal loss.
Proper sizing of wires is crucial: undersized cables can overheat and cause voltage drops, lowering system efficiency and risking damage.
Weatherproof connectors and secure mounting prevent corrosion and mechanical failures, ensuring long-term, reliable operation.
Summarized Energy Flow in Your RV Solar System:
Sunlight → Solar Panels generate DC electricity → Charge Controller regulates flow → Batteries store energy → Inverter converts DC to AC → Appliances powered
Why Understanding this Flow Matters
Knowing how these components work together helps you troubleshoot problems, optimize your system’s performance, and make smart upgrades in the future.
For example, if your batteries aren’t charging fully, the issue might be in the charge controller or panel wiring. Or if appliances are not running smoothly, checking inverter output quality is key.
Being informed empowers you to enjoy your RV solar system confidently wherever you travel.
- Solar panels capture sunlight and create DC electricity.
- DC power goes to the charge controller, which manages voltage to safely charge the battery bank.
- The batteries store electricity for use when the sun isn’t shining.
- When you plug in devices or appliances, the inverter converts DC electricity from the batteries to AC electricity.
- Wiring connects all parts safely, and mounting hardware keeps panels secure.
Tips for Choosing RV Solar Panel System Components
Choosing the right components for your RV solar panel system is essential for building a reliable, efficient setup that meets your power needs on the road. Here are some important tips to help you make informed decisions:
1. Determine Your Energy Needs First
Before buying any solar equipment, calculate the total energy your RV uses daily. Make a list of all the appliances and devices you plan to run on solar power, such as lights, fridge, fan, and charging electronics. Check their power ratings (in watts) and estimate how many hours per day each will run. Adding these up will give you the total watt-hours you need to produce and store. This helps you choose solar panels, batteries, and inverters sized correctly for your lifestyle.
2. Choose Solar Panels That Fit Your Roof and Budget
RV roof space is limited, so selecting solar panels that provide the greatest power output for their size is crucial. Monocrystalline solar panels are generally the most efficient and compact, making better use of your roof area. Polycrystalline panels cost less but take up more space for the same wattage.
If your roof has curves or obstructions, consider flexible solar panels that can bend and weigh less, although they tend to be less efficient and more expensive per watt.
3. Invest in an Efficient Charge Controller
The charge controller prevents batteries from overcharging and protects them from damage. MPPT (Maximum Power Point Tracking) charge controllers are more advanced and efficient compared to PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) controllers. MPPT controllers extract more power from your solar panels—often 10%-30% more—by optimizing the voltage and current.
While MPPT controllers cost more upfront, they deliver better performance, especially in cloudy weather or with longer cable runs, making them a smart investment.
4. Pick Batteries Based on Weight, Capacity, and Maintenance Needs
Batteries store the solar energy you collect. Since weight is a key factor in RVs, lithium-ion batteries are often preferred for their light weight, long life, and minimal maintenance. They provide more usable capacity and can be discharged deeper without damage.
Lead-acid batteries are more affordable and widely available, but are heavier and require regular maintenance, like checking electrolyte levels. They also have shorter lifespans.
Choose batteries based on your budget, desired system autonomy (how long you can run without sun), and willingness to perform maintenance.
5. Use a Pure Sine Wave Inverter for Sensitive Electronics
The inverter converts the DC power stored in batteries to AC power used by most household appliances. Pure sine wave inverters provide clean, smooth power matching utility electricity, ideal for sensitive devices such as laptops, medical equipment, and microwaves.
Modified sine wave inverters are cheaper but produce a rougher power waveform, which can cause noise or reduce the lifespan of some electronics.
For RV owners who rely on modern electronics, a pure sine wave inverter is highly recommended despite the higher cost.
6. Ensure All Wiring and Connections Are Rated for RV Use
Using high-quality, RV-rated wire and connectors helps maintain system efficiency and safety on the road. Wires sized appropriately for your current and distance prevent power loss and overheating.
Make sure connectors are weatherproof and properly sealed to avoid corrosion or shorts, especially since RVs are exposed to various outdoor environments.
7. Select Mounting Hardware That Fits Your RV Roof and Solar Panels
Your solar panels need secure mounting to withstand wind, vibration, and road movement. Choose mounting brackets appropriate for your type of panels and roof material—metal roofs, fiberglass, or rubber roof RVs require different mounting solutions.
Some RV owners prefer low-profile or flush mounts to keep a sleek look and reduce wind drag. Others may use adjustable mounts to change panel angles for better sun exposure when parked.
By carefully considering these tips, you can build an RV solar panel system tailored to your unique travel style and energy requirements. A well-designed system ensures you enjoy off-grid freedom with reliable, renewable power.
Conclusion
Understanding the main components of an RV solar panel system is key to designing a solar setup that keeps your RV powered wherever your travels take you. From selecting the right panels to choosing batteries and controllers, each piece plays a vital role in creating an efficient, reliable off-grid power source.
By choosing quality components tailored to your specific needs, you’ll enjoy the freedom and convenience of solar-powered RV living with confidence.
FAQs
Yes, with basic electrical knowledge and the right tools, many RV owners install solar systems DIY, but professional help is recommended for complex setups
MPPT controllers are more efficient, especially in colder or less sunny conditions, but cost more than PWM controllers.
Lead-acid batteries last 3-5 years, while lithium-ion batteries can last 10 years or more with proper care.
