Diesel vs Solar Generators Full Comparison, Costs, and Best Uses

Discover the comparison of diesel vs solar generators, including costs, pros, cons, and best uses, to choose the right power solution for you.
Introduction: Diesel vs Solar Generators
Diesel generators provide consistent power, especially in situations requiring high output or when solar power is unavailable, but they are noisy, pollute the environment, and have ongoing fuel costs. Solar generators, on the other hand, are environmentally friendly, quiet, and offer free fuel (sunlight), but their power output can be limited by weather conditions, and they may require a larger initial investment.
What are diesel generators?
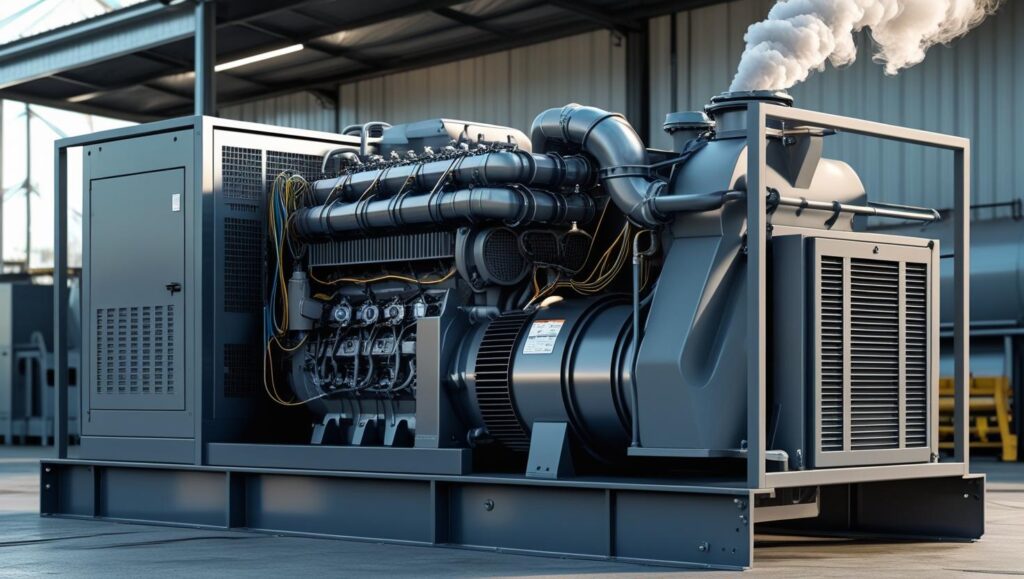
Diesel Generator
A diesel generator is a combination of a diesel engine and an electrical generator, used to produce electrical energy. They are commonly used as a reliable source of backup power for homes, businesses, and industrial facilities. They are known for their fuel efficiency and longevity, especially for heavy-duty and long-term use.
How diesel generator work?
A diesel generator works by converting the chemical energy in diesel fuel into electrical energy through a combination of mechanical movement and electromagnetic induction.
step-by-step process:
Fuel Combustion
- Diesel fuel is injected into the engine cylinder.
- Compressed air in the cylinder gets extremely hot (due to high compression ratio), causing the diesel to ignite without a spark plug.
- This controlled explosion pushes the piston down.
Mechanical Energy Creation
- The pistons’ up-and-down motion turns the crankshaft.
- The crankshaft’s rotation drives the rotor inside the generator’s alternator.
Electrical Generation (Electromagnetic Induction)
- As the rotor spins inside a stationary stator (coil of wire), it creates a magnetic field.
- This movement induces an electrical current in the stator windings.
Voltage Regulation
- The output passes through a voltage regulator to ensure a steady voltage suitable for your devices.
Power Output
- The generator delivers AC electricity (or DC if converted) to power equipment, homes, or backup systems.
Key Points:
- Diesel engines are durable and can run for long hours.
- They are more fuel-efficient than gasoline engines for heavy-duty use.
- Require regular maintenance (oil changes, filter cleaning, fuel checks).
Key Features and Benefits:
- Reliability: Diesel generators are known for their dependability, particularly in emergencies and for long-term operation.
- Fuel Efficiency: They often offer better fuel economy compared to gasoline generators, especially when running at or near full load.
- Durability: Diesel engines are generally robust and designed to last for extended periods, making them suitable for demanding applications.
- Heavy-Duty Performance: Diesel generators are well-suited for handling large loads and continuous operation, making them ideal for industrial and commercial applications.
- Lower Running Costs: While the initial cost might be higher, the lower fuel consumption and potentially longer lifespan can lead to lower overall running costs, according to Electric Generators Direct.
Types of Diesel Generators:
- Portable Generators: These are smaller, often wheeled units used for temporary power needs at construction sites, events, or as backup power for homes.
- Standby Generators: These are larger, permanently installed units that automatically switch on when main power is lost, providing continuous power to essential loads.
- Inverter Diesel Generators: These offer quieter operation and greater fuel efficiency compared to standard diesel generators.
- Commercial and Industrial Generators: These are large-scale units designed for powering entire facilities or critical infrastructure.
Common Applications:
- Backup Power: Diesel generators are widely used to provide power during outages for homes, businesses, hospitals, and data centers.
- Primary Power Source: In remote areas or off-grid locations, diesel generators can be the primary source of electricity.
- Peak Shaving: Some facilities use diesel generators to reduce their peak electricity demand, lowering overall energy costs.
- Construction Sites: Portable diesel generators provide power for tools, equipment, and lighting on construction projects.
- Mobile Applications: Diesel generators can be used in vehicles or trailers for various purposes, such as powering construction equipment or providing electricity for events.
Diesel Generators: Pros, Cons & Uses
- Pros of Diesel Generators:
- High Power Output:
Diesel generators are designed to deliver large amounts of power consistently, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications such as industrial operations, construction sites, and large-scale backup systems. They can handle high-load demands without performance drops. - Reliability:
These generators are known for their durability and ability to run for long periods without failure. Diesel engines are less likely to stall under heavy loads and can perform well in harsh weather conditions, ensuring power when it’s most needed. - Widespread Availability:
Diesel fuel is easily accessible in most regions worldwide, making it convenient to refuel, even in remote areas. This is a major advantage during emergencies or in off-grid locations where other fuel sources might be scarce. - Low Upfront Cost:
Compared to solar generators with similar power capabilities, diesel units generally require a lower initial investment. This makes them appealing for businesses or individuals needing immediate power solutions without high startup expenses. - Best For: heavy loads, emergency backup in remote areas, and industrial sites.
- Cons of Diesel Generators:
- Fuel Costs:
While diesel generators are relatively efficient in terms of fuel-to-power conversion, the cost of diesel fuel can add up quickly, especially with prolonged use. This makes long-term operation more expensive compared to renewable options. - Noise:
Diesel engines are noisy, which can be disruptive in residential areas, camping sites, or quiet work environments. Noise-reduction enclosures can help, but they add to the overall cost. - Maintenance:
Regular servicing is essential for diesel generators, including oil changes, fuel filter replacements, and checking mechanical components. Neglecting maintenance can lead to costly repairs and reduced lifespan. - Emissions:
Diesel generators produce carbon dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter, contributing to air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. This environmental impact is a major drawback compared to clean-energy alternatives like solar.
What are solar generators?

Solar Generators
Solar generators combine solar panels with a battery system and an inverter to provide portable, renewable power. They convert sunlight into electricity, which is then stored in a battery for later use to power devices and appliances. This makes them a versatile option for off-grid power, emergency backup, and outdoor activities.
How Solar Generators Work:
- Solar Panel Conversion: Solar panels, typically made of photovoltaic cells, capture sunlight and convert it into direct current (DC) electricity.
- Charge Controller: The DC electricity is then routed to a charge controller, which regulates the power flow to the battery and prevents overcharging.
- Battery Storage: The battery stores the DC electricity for later use, providing a backup power source.
- Inverter: An inverter converts the stored DC electricity into alternating current (AC) electricity, which is compatible with most household appliances and devices.
Key Components:
- Solar Panels: Capture sunlight and generate DC electricity.
- Charge Controller: Regulates power flow to the battery.
- Battery: Stores the DC electricity.
- Inverter: Converts DC to AC electricity.
Benefits:
- Portability: Solar generators are often compact and easy to transport, making them suitable for camping, tailgating, and other outdoor activities.
- Renewable Energy: They utilize solar power, a clean and sustainable energy source.
- Quiet Operation: Unlike traditional generators, solar generators operate quietly, without producing exhaust fumes.
- Emergency Backup: They can provide a reliable power source during power outages.
Factors to Consider:
- Capacity: Measured in Watt-hours, capacity determines how much power the generator can store and how long it can power devices.
- Output: Measured in Watts, output indicates the maximum power the generator can deliver at any given time.
- Durability and Brand: Choose reputable brands for reliability and longevity.
- Expandability: Some systems allow for expansion with additional solar panels or batteries.
Solar Generators: Pros, Cons & Uses
- Pros of Solar Generators:
- Clean Energy:
Solar generators harness energy from the sun, producing electricity without emitting greenhouse gases, noise, or harmful pollutants. They’re an environmentally friendly alternative to fossil-fuel-powered units, helping reduce your carbon footprint and supporting sustainability goals. - Quiet Operation:
Unlike diesel generators, solar units have no combustion engine, so they operate almost silently. This makes them perfect for residential areas, camping trips, RVs, or any setting where noise reduction is important. - Low Running Cost:
After the initial purchase, the operating cost is minimal. Sunlight is free, and the only ongoing expenses might involve occasional battery maintenance or replacement every few years. This makes them economical in the long term, especially in sunny climates. - Scalable Setups:
Solar generator systems can be easily expanded by adding more solar panels or battery storage. This scalability allows users to start small—powering only essential devices—and gradually grow the system to meet increased energy needs.
- Cons of Solar Generators:
- Higher Upfront Cost:
Quality solar generators and battery storage systems can have a significant initial price tag. While costs are dropping each year, the upfront investment is still higher than many diesel generators of similar capacity. - Dependence on Sunlight:
Solar generators rely on sunlight to charge, so their performance is affected by weather conditions and seasonal variations. In areas with prolonged cloudy days or limited daylight, charging efficiency may drop. - Battery Limitations:
Solar generators store power in batteries, which have limited capacity. Once the battery is drained, it needs recharging before more power is available. Additionally, batteries require replacement every 5–10 years, adding to long-term costs. - Best For: camping, off-grid homes, and environmentally conscious users.
- Head-to-Head Comparison: Diesel vs Solar generator:
| Feature | Diesel Generator | Solar Generator |
| Upfront Cost | Low–Medium | Medium–High |
| Operating Cost | High ( fuel, maintenance ) | Low (sunlight, batteries) |
| Power Output | High, consistent | Moderate, variable with sunlight |
| Environmental Impact | High (emissions, noise) | Low (zero emissions, quiet) |
| Maintenance Frequency | High (oil changes, parts) | Low (battery care, occasional checks) |
| Best Use Case | Heavy-duty backup, industrial settings | Off-grid living, households, RVs |
Cost Analysis: Diesel vs Solar Generators
When deciding between diesel generators and solar generators, it’s important to look beyond just the purchase price. The true cost includes fuel, maintenance, repairs, and long-term operation over the generator’s lifespan.
1. Upfront Cost
- Diesel Generators – Generally less expensive to purchase initially. A mid-range unit can cost between $1,000 and $5,000, depending on power capacity. This lower entry price makes diesel appealing for immediate or short-term power needs.
- Solar Generators – Have a higher initial investment due to solar panels, batteries, and inverter systems. Quality setups range from $1,500 to $10,000+ based on size and battery storage capacity.
2. Operating Costs
- Diesel Generators – Require ongoing fuel purchases. Running a 5 kW diesel generator for 8 hours a day could cost $10–$20 daily in fuel, depending on diesel prices in your region. Over a year, this adds up significantly.
- Solar Generators – Sunlight is free, so daily running costs are nearly zero. The only recurring expenses are related to battery replacements every 5–10 years, which typically cost $500–$2,000.
3. Maintenance & Repairs
- Diesel Generators – Need regular oil changes, filter replacements, and periodic servicing to prevent breakdowns. These costs can range from $150–$500 annually for moderate use.
- Solar Generators – Minimal maintenance is required, mainly keeping solar panels clean and monitoring battery health. Annual costs are usually negligible unless a component needs replacing.
4. Lifespan & Long-Term Value
- Diesel Generators – Can last 10–15 years with proper care, but fuel and maintenance costs make them more expensive in the long run, especially for frequent use.
- Solar Generators – Panels can last 20–25 years, while batteries may need replacement during that time. Despite the higher initial price, the low operating cost means solar often becomes more economical after 5–7 years of consistent use.
5. Total Cost of Ownership (10-Year Estimate)
| Generator Type | Initial Cost | Operating & Maintenance Cost (10 yrs) | Total Estimated Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diesel Generator | $3,000 | ~$20,000+ (fuel + maintenance) | ~$23,000 |
| Solar Generator | $6,000 | ~$2,000 (battery replacement) | ~$8,000 |
Note: Actual costs vary by location, usage patterns, fuel prices, and the quality of equipment.
Conclusion
Diesel and solar energy each serve distinct needs. Diesel power offers high, consistent output and works anywhere, anytime—making it reliable for heavy-duty or backup use—but it comes with ongoing fuel costs, noise, and environmental drawbacks.
Solar energy provides clean, quiet, and low-maintenance power with no fuel expense, but it requires a higher initial investment and relies on sunlight availability. The right choice depends on your priorities—whether you value immediate affordability and power reliability, or long-term savings and sustainability.
FAQs: diesel vs solar generators
It depends on your needs. Diesel generators offer higher and more consistent power output, making them ideal for heavy loads and industrial use. Solar generators are cleaner, quieter, and have lower operating costs, making them better for eco-friendly, long-term power solutions.
Yes, diesel generators generally have a lower upfront cost. However, over time, solar generators can be more cost-effective because they have no fuel costs and require less maintenance
Solar generators rely on stored battery power, so they can work at night or during cloudy weather if the batteries have been charged sufficiently during sunny periods
Diesel generators produce carbon emissions, noise, and sometimes harmful particulates. Solar generators produce no direct emissions, making them a cleaner alternative.
In most industrial or high-demand settings, diesel generators are still preferred due to their consistent power output. Solar generators are better suited for off-grid homes, camping, RVs, and light-to-moderate energy needs.
