How Many 200 Ampere Breakers Fit in a 200 Amp Panel?

Discover how many 200-ampere breakers fit in a 200-amp panel, breaker sizes, panel capacity, and safety tips. Learn everything about 200 amp panels & upgrades today!
Ever wondered how many electrical breakers are in a 200-amp panel? It’s a common question, and understanding the answer is crucial for maintaining a safe and efficient electrical system in your home in 2025. Buckle up, because we’re looking into the fascinating world of electrical panels and breakers!

What is a 200-amp panel?
A 200 200-amp panel, also known as a service panel or breaker box, is the central hub of a home’s electrical system. It acts as the gateway, distributing electrical power to various circuits throughout the house. It serves as the primary distribution point for electricity in residential or commercial buildings. This panel contains circuit breakers that regulate the flow of electricity, ensuring safety.
The term “200 amp” refers to the panel’s capacity to handle electrical current. It signifies that the panel can safely accommodate up to 200 amps of electricity flowing through it. This capacity is suitable for most average-sized homes and small commercial establishments. However, larger buildings may require higher amp panels to meet their energy demands.
How much load can a 200-ampere breaker handle?
A 200-Amp Panel Supports up to 48,000 Watts
If all of the circuit breakers in your electrical panel are 120 V, multiply that by 200 amps to yield 24,000 watts. Theoretically, a 240 V breaker will support up to 48,000 watts. Your electrical system should run at a maximum of 80 percent capacity.
How Many Breakers Are in a 200-ampere Panel?
If you’re using single-pole breakers, a 200-amp electrical panel will typically have 40 to 42 slots. When double pole breakers are used, the unit will have 20 slots. Depending on the amperage of the appliances used in your home, using too many at once may overload the system.
How many volts are in 200 amperes?
A 200-amp panel can handle up to 200 amps of current at 240 volts between the two hot wires. However, this does not mean that you can use all 200 amps at once. You should leave some margin for safety and avoid overloading your panel.
How much current can a 200-circuit can handle?
A 200-amp panel can handle up to 200 amps of current at 240 volts between the two hot wires. However, this does not mean that you can use all 200 amps at once.
Leave some margin for safety and avoid overloading your panel. A good rule of thumb is to use no more than 80% of your panel’s capacity at any given time.
This means that you should limit your total load to about 160 amps at 240 volts or 320 amps at 120 volts. You can distribute this load among different circuits and breakers in your panel.
For example, you can have two 100-amp breakers for two subpanels, or four 50-amp breakers for four appliances.
The primary function of a 200-ampere panel
A 200-amp panel primarily functions as the main distribution center for electrical power in a residential or commercial building. Its key roles include:
- Receiving Electricity from the Utility:
The panel acts as the gateway through which electrical current from the utility company’s power lines enters the building, safely channeling the incoming electricity. - Distributing Power to Circuits:
Inside the panel, circuit breakers divide the electricity into multiple branch circuits that supply different parts of the building, such as lighting, outlets, appliances, and HVAC systems. - Protecting the Electrical System:
Circuit breakers in the panel automatically shut off power in case of overloads or short circuits, preventing electrical fires, wiring damage, and other hazards. This built-in safety mechanism ensures that individual circuits do not carry currents beyond their rated capacity. - Handling a Maximum Safe Current of 200 Amps:
The “200 amp” rating indicates that the panel can safely carry and manage up to 200 amperes of continuous electrical current without overheating or failure, which is suitable for most average-sized homes and light commercial properties. - Providing Capacity for Future Expansion:
With typically 40 to 42 breaker slots, a 200 amp panel supports multiple circuits and allows for adding additional devices or upgrades, such as electric vehicle chargers or solar power systems, without requiring major panel replacement.
So, the primary functions of a 200 amp panel are to receive, distribute, and protect electrical power while safely managing a high current load to keep your building’s electrical system reliable and hazard-free.
circuit breaker …your silent guardian
Why are Breakers Important?
Think of a breaker as a superhero with a super-sensitive power gauge. When too much electricity flows through a circuit (like too many cars on a narrow street), the breaker trips, cutting off the power and preventing dangerous fires or equipment damage. It’s like a silent guardian, always watching over your electrical safety.
Safety assurance
To ensure safety, a 200-amp circuit breaker panel is equipped with multiple circuit breakers. These breakers act as electrical panels’ protective devices, automatically shutting off the power in case of an overload or short circuit. They prevent electrical fires and damage to the electrical system. Each circuit breaker corresponds to a specific branch circuit, allowing for individual control and protection.
crucial signs to update your service panel
There are also crucial signs that suggest you should update your service panel sooner rather than later, such as:
Your home has modern new technology in it, and the panel is old technology
Appliances are not operating at their maximum potential.
Lights throughout your home flicker and dim.
Not enough power from outlets to meet demand.
Switches and outlets appear damaged or worn.
The panel is corroded, water-damaged, or the breakers don’t work.
You’re planning to remodel your home.
You are planning on adding additional loads to the home.
The Cost to Upgrade an Electrical Panel?
The electrical panel is the heart of your home’s electrical system. It’s where the power from the utility company enters your home and is distributed to the various circuits.
But like any other component of your home, it can become outdated or insufficient over time.
Upgrading your electrical panel can be a significant investment. It’s not just about buying a new panel and plugging it in. There are many factors to consider, from the size of the panel to the labor costs to replace the electrical panel involved in the installation.
Factors that determine how many breakers are installed in a 200-ampere panel:
Panel Slot Capacity (Spaces):
Panels come with a fixed number of breaker slots or spaces. Typical 200-amp panels usually have from 30 to 42 spaces, with each slot able to hold a single-pole breaker or two slots used by a double-pole breaker. The total number of breakers depends on the number of available spaces.
Breaker Types and Sizes:

200 amp breaker sizes
Single-pole breakers (usually 15–20 amps) occupy one slot and serve standard 120V circuits (lighting, outlets).
Double-pole breakers (usually 30–60 amps) occupy two adjacent slots and handle 240V loads (HVAC, electric ranges).
Tandem breakers can provide two circuits in one slot, increasing circuit count without adding physical slots.
The combination of breaker types determines the total number of circuits possible.
Bus Bar Ampere Rating (Panel Rating):
The panel’s bus bar or bus assembly defines the maximum current rating (200 amps in this case) that the panel can handle safely. This rating does not directly limit the number of breakers but limits the total amperage flowing through the panel.
Electrical Load Calculations and Balancing Across Phases:
Panels have alternating phases (A and B for single-phase, A, B, and C for three-phase) fed by the bus bars. To prevent overload, breakers must be arranged to balance loads between phases, ensuring total simultaneous current does not exceed 200 amps.
The fact that multiple breakers total more than 200 amps does not mean the panel is overloaded, because not all circuits run at full capacity simultaneously, and double-pole breakers use current from two phases.
National and Local Electrical Codes:
Compliance with NEC (National Electrical Code) rules governs breaker sizing and placement. Code requires safety margins (typically using the 80% rule), proper breaker sizing for continuous loads, and appropriate panel capacity for the expected load.
Future Expansion and Load Requirements:
The number of breakers also depends on anticipated future expansion or additions like electric vehicle chargers, solar power systems, or new appliances, leading to either more circuits or a need for subpanels.
Breaking Down the Breakers: Understanding Different Types of Circuit Breakers
Circuit breakers are essential components in any electrical system, safeguarding the wiring and devices from overloads and short circuits. Different types of breakers serve various purposes depending on current rating, location, and protection type.
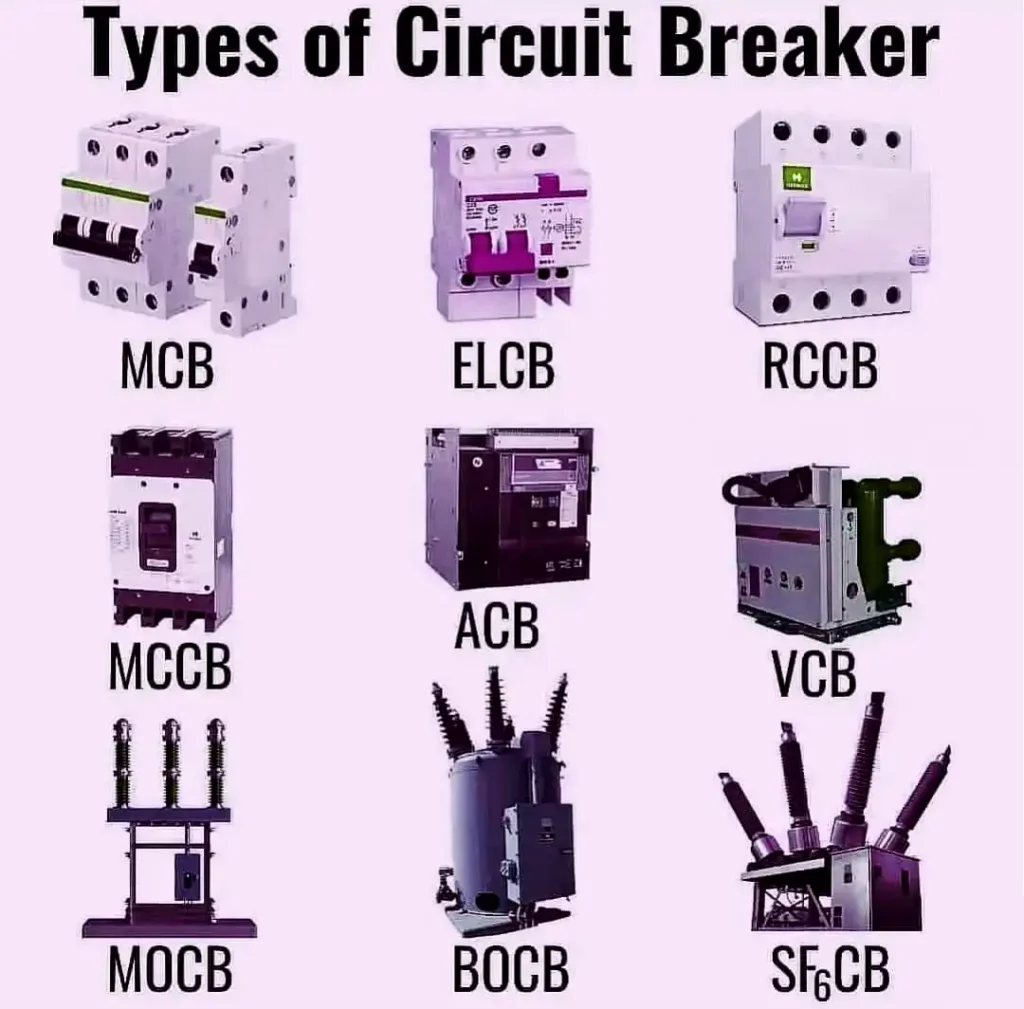
1. Miniature Circuit Breakers (MCBs)
- Overview: Compact breakers are designed for low-current residential and small commercial circuits, typically ranging between 6 to 63 amps.
- Applications: Lighting circuits, general household outlets, and office plug sockets.
- Key Benefits: Reliable overload and short-circuit protection for everyday electrical needs.
2. Molded Case Circuit Breakers (MCCBs)
- Overview: Rugged, adjustable trip setting breakers capable of handling higher current loads, typically used in commercial and industrial settings.
- Applications: Large commercial buildings, industrial machinery, warehouse facilities.
- Key Benefits: Flexibility through adjustable trip settings and robust protection.
3. Residual Current Circuit Breakers (RCCBs)
- Overview: Breakers that detect leakage currents possibly caused by faulty insulation or moisture instantly disconnect to prevent electrocution.
- Applications: Bathrooms, kitchens, outdoor outlets, swimming pool areas.
- Key Benefits: Enhanced safety against ground faults and shocks.
4. Arc Fault Circuit Interrupters (AFCIs)
- Overview: Designed to detect and interrupt arcing faults in electrical wiring, a major cause of electrical fires.
- Applications: Bedrooms, living areas, places prone to wiring deterioration or damage.
- Key Benefits: Fire prevention by detecting dangerous arc faults early.
5. Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters (GFCIs)
- Overview: Specialized breakers that quickly trip upon detecting current leakage to ground, protecting against electric shock.
- Applications: Outdoor outlets, kitchens, bathrooms, and damp locations.
- Key Benefits: Life-saving protection in wet or high-risk environments.
6. High-Voltage and Specialized Circuit Breakers
- Air Circuit Breakers (ACBs): Use air as the arc-quenching medium, employed in high current applications (up to several thousand amps).
- Oil Circuit Breakers: Use mineral oil to extinguish arcs, commonly found in medium voltage applications.
- SF6 Gas Circuit Breakers: Utilize sulfur hexafluoride gas for superior arc extinction in high-voltage switchgear.
- Vacuum Circuit Breakers: Extinguish arcs in vacuum chambers, reducing wear and improving reliability.
7. Specialized Trip Characteristics (MCB Types)
- Type B: Trips at 3-5 times rated current; ideal for residential and resistive loads.
- Type C: Trips at 5-10 times; suited for inductive loads like small motors.
- Type D: Trips at 10-20 times; used for heavy industrial motors.
- Type K & Z: Used for sensitive and specific industrial or medical equipment.
Summary Table of Common Breaker Types and Their Uses
| Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB) | 6-63 A | Residential lighting, small loads | Compact, quick reset |
| Molded Case Circuit Breaker (MCCB) | Up to 1600 A | Commercial, industrial machinery | Adjustable trip, high capacity |
| Residual Current Circuit Breaker (RCCB) | Varies | Leak detection, human safety | Protection from earth faults |
| Arc Fault Circuit Interrupter (AFCI) | Varies | Fire-prone areas (bedrooms) | Detects arc faults |
| Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI) | Varies | Wet areas/outdoor locations | Protects from shocks |
| Air/Oil/SF6/Vacuum Breakers | High voltage & amperes | Utility substations, industrial | High voltage arc quenching |
Breakers come in different sizes, just like people wear different shoe sizes. Smaller breakers (15-20 amps) handle low-powered things like lights and TVs, while bigger ones (30-60 amps) are for power-hungry appliances like ovens and air conditioners. The key is to match the breaker size to the maximum load of each circuit.
Factors that Influence the Number of Breakers
The number of breakers you need ultimately depends on your electrical needs and plans. Do you have an electric stove? Do you dream of adding a hot tub someday? These factors will influence how many circuits you need, and therefore, how many breakers you’ll need to fit your power demands.
Safety First, Always
Electrical work is no joke. Installing or modifying your panel should always be done by a qualified electrician who understands the complex rules and regulations governing electrical safety. Think of them as the experienced electricians who maintain the city’s power grid, ensuring everything runs smoothly and safely.
Warning Signs of Overload
A 200-amp panel can handle a lot, but pushing it too far can lead to trouble. Look out for warning signs like flickering lights, tripped breakers, or even burning smells. These could be clues that your panel is overloaded and needs attention.
Upgrading Your Power Game
If your electrical needs grow beyond the capacity of your breakers in a 200-amp panel, don’t fret! Upgrading to a higher-capacity panel is possible, but it’s a job for the pros. An electrician can assess your needs and recommend the best course of action for your home’s electrical future.
The Future of Smart Power
Modern panels are embracing smart technology, introducing smart breakers that monitor energy usage and even allow remote control. These innovations can help you optimize your energy use and save on your electricity bills, making your home both smarter and more eco-friendly.
Going Green with Smart Breakers

going green with smart breakers
Choosing energy-efficient appliances and smart breakers can not only save you money but also contribute to a more sustainable future. Every little bit counts when it comes to reducing your home’s environmental impact.
Real-Life Examples and Lessons Learned
From successfully managing a 200-amp panel in a small apartment to the challenges and benefits of upgrading to a larger system, real-life case studies offer valuable insights and lessons for homeowners like you. Learn from the experiences of others and make informed decisions about your electrical system.
The Future of Panels is Bright
The world of electrical panels is constantly evolving, with innovations like intelligent load management and integrated renewable energy sources on the horizon. Stay curious and informed about these exciting developments to ensure your home’s electrical system remains efficient and future-proof.
Conclusion
Adding more breakers can compromise electrical system safety if done incorrectly or without proper load management. It’s essential to assess your panel’s capacity, perform accurate load calculations, adhere strictly to electrical codes, and use professional installation to maintain safe and reliable operation. Regular inspections and timely upgrades ensure your home’s electrical system remains secure and efficient.
Understanding how many breakers fit in a 200-amp panel is just one step towards mastering your home’s electrical system. By prioritizing safety, choosing the right equipment, and keeping an eye on the future, you can ensure a reliable and efficient flow of power for years to come. Remember, knowledge is power, and when it comes to electricity, that’s true!
Concerned about your electrical panel’s safety or considering adding more breakers? Contact a licensed electrician today for a professional assessment and upgrade to keep your home safe and code-compliant.
Also Explore: Momentum Solar Pyramid Scheme, COST, FACTS (Updated 2024)
FAQs
Around 40, but it depends on breaker sizes and specific models. Always consult an electrician for your unique needs.
Absolutely not! Exceeding the 200 amp limit can be dangerous and cause electrical overloads.
Flickering lights could be a sign, but other factors may also be at play. Consult an electrician for proper diagnosis and solution.
Yes, they can offer energy savings, remote control, and enhanced safety features. Explore the options and see if they align with your needs!
At least every 3-5 years or when adding new circuits to ensure safety and code compliance.
Implementing breakers responsibly protects your home, appliances, and loved ones from electrical hazards. Always consult professionals for electrical work to ensure safety and avoid costly risks.
Overloading may cause breakers to trip frequently or fail to protect circuits, risking overheating or electrical fires.
