Risk of Solar Panels a Dark Side unveiled
Explore the hidden risks and dark side of solar panels. Safety concerns, environmental, and maintenance challenges you should consider in 2025.
Rooftop solar power is often lauded as a clean energy solution; however, it has some downsides that are often overlooked.
These include the high upfront cost of installation, the intermittency of solar energy (it only works when the sun shines), potential for poor customer service from some companies, and the eventual challenge of disposing of solar panel waste.
Solar panels have a darker side
1. High Initial Costs and Financing Challenges:
- Upfront Investment:
Installing rooftop solar panels requires a significant upfront investment, which can be a barrier for some homeowners. - Financing Models:
To make solar more accessible, companies have developed various financing models. However, these can sometimes lead to complex contracts and hidden costs, potentially leaving some customers feeling misled.
2. Intermittency and Storage Limitations:
- Sunshine Dependent:
Solar panels only generate electricity when the sun is shining. This means that during cloudy days or at night, solar power is not available, requiring reliance on other energy sources or battery storage. - Battery Storage Costs:
Battery storage solutions, which can help mitigate the intermittency issue, can be expensive and may not be sufficient to store large amounts of energy.
3. Customer Service Issues:
- Poor Installation and Maintenance:
Some homeowners have reported issues with the quality of installation and difficulty getting timely repairs or maintenance for their solar panels. - Aggressive Sales Tactics:
In the rush to install solar panels, some companies have been accused of using aggressive sales tactics, leaving customers with a negative experience.
4. Waste Management Challenges:
- End-of-Life Disposal:
Solar panels have a limited lifespan, and the industry is still developing effective and sustainable ways to recycle or dispose of them at the end of their useful life. - Limited Recycling Capacity:
The current capacity to recycle solar panels is limited, and the panels contain materials that can be difficult and costly to recover. - Value of Materials:
While panels contain some valuable materials, the majority is made of glass, a low-value material, which can disincentivize recycling efforts.
5. Other Considerations:
- Land Use:
While rooftop solar minimizes land use, large-scale solar farms can require significant land areas, potentially impacting ecosystems. - Manufacturing Impacts:
The manufacturing process of solar panels can have environmental impacts, including energy consumption and the use of certain chemicals.
In short, while solar energy is a crucial part of the transition to a cleaner energy future, it’s important to acknowledge its limitations and address the challenges associated with its widespread adoption.
By improving manufacturing processes, developing better recycling technologies, and ensuring fair business practices, the industry can move towards a more sustainable and equitable future.
Panels, Panels Everywhere

Solar panels every where
It is easier for people to trade their old solar panels for new ones that work better and cost less.
In solar energy, we don’t have good ways to recycle old panels yet. Because of this, throwing away so many panels could become a big problem that hurts the environment a lot.
Official reports do not always tell this story. The International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) says that by the early 2030s, there will be a lot of solar panel trash every year, and by 2050, it could add up to 78 million tons.
That’s a shocking amount, undoubtedly. But with so many years to prepare, it describes a billion-dollar opportunity for the recapturing of valuable materials rather than a dire threat.
The threat is hidden by the fact that IRENA’s predictions are premised upon customers keeping their panels in place for the entirety of their 30-year life cycle. They do not account for the possibility of widespread early replacement.
The negative aspect of solar panels
While solar energy itself is clean, the production of solar panels and batteries can have environmental drawbacks. Manufacturing these components requires large amounts of energy, often sourced from fossil fuels, which contributes to greenhouse gas emissions.
Fire risks with Solar panels
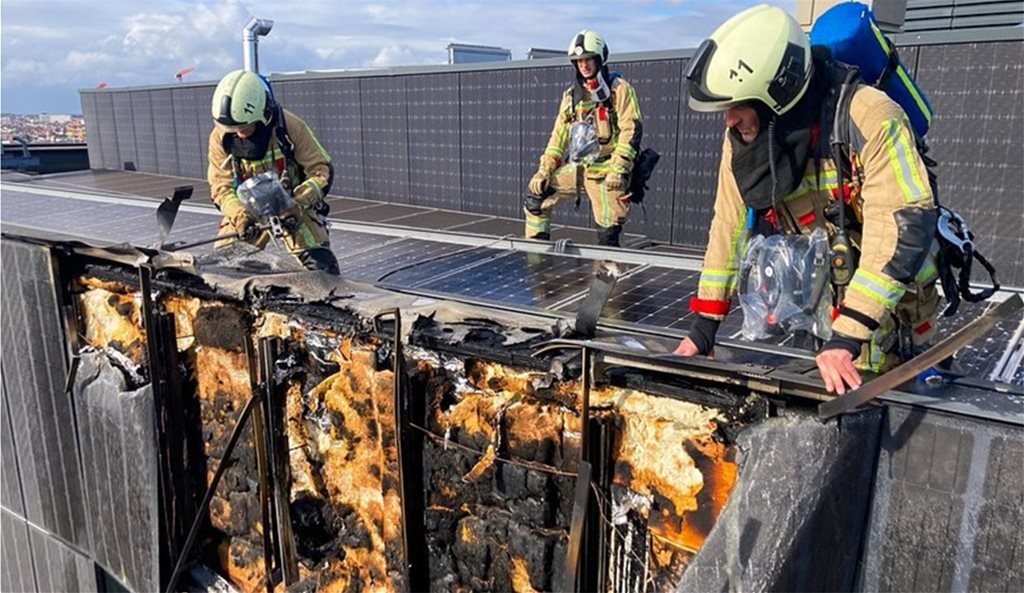

risk of fire with solar panels
Low-quality and incorrectly installed solar systems can cause fires, just like any other installed electrical device. This is why workmanship is so important, it lessens the risk of solar panels.
A safe solar system is important for both you and us; we hate the idea that a system we worked on could cause a fire and any damage or harm.
Solar system-related fires do happen, but nationwide, the number of fire incidents with solar is below 1%. Incorrect installation is the primary cause of issues.
Risks discussed on Reddit
The risks of Solar panels and disadvantages, as discussed on Reddit, include high upfront costs, long payback periods, and potential complications with roof repairs and replacements.
Furthermore, solar panels may not be aesthetically pleasing to some homeowners. While solar panels offer environmental benefits, they also raise concerns about their production and disposal.
few discussed below
Financial Risks:
- High upfront cost:
Solar panel systems can be expensive to purchase and install. - Long payback period:
It can take many years for the energy savings to offset the initial investment. - Dependence on government incentives:
The economics of solar panels can be heavily influenced by government incentives and rebates, which can change. - Home value impact:
While solar panels can increase home value, the increase may not always match the initial cost of the system, particularly if the system is leased or financed. - Potential for roof leaks:
Improper installation or the weight of the panels can potentially cause roof leaks, which can be costly to repair. - Disposal costs:
Solar panels have a lifespan, and disposal at the end of their life cycle can also incur costs.
Practical Considerations:
- Efficiency and weather dependency:
Solar panel output is dependent on sunlight, so they are less efficient on cloudy days, at night, or during winter. - Intermittency:
Solar energy is intermittent, meaning it’s not always available when needed, requiring either battery storage or reliance on the grid. - Roofing issues:
Replacing a roof with solar panels installed can be a complex and expensive process. - Aesthetics:
Some homeowners dislike the look of solar panels on their roofs. - Maintenance:
Solar panels require occasional cleaning and maintenance to maintain optimal performance. - Pest problems:
Birds, particularly pigeons, may nest under solar panels, potentially causing damage and requiring pest control. - Grid dependency:
Without battery storage, solar panels rely on the grid for power during outages.
Environmental Concerns:
- Production pollution:
The manufacturing of solar panels requires energy and can involve the use of some harmful chemicals. - Disposal concerns:
While efforts are underway to recycle solar panels, disposal can still pose environmental challenges. - Land use:
Large-scale solar farms can impact land use, potentially affecting agriculture or requiring deforestation.
| Cons of Solar Panels | Explanation |
| High Initial Cost | Solar panel systems, including installation, can cost thousands of dollars upfront ($12,000-$31,000 typical), which is a barrier for many homeowners. |
| Weather Dependence | Solar panels only generate electricity during daylight and are less effective on cloudy, rainy, or snowy days, reducing reliability in some climates. |
| Energy Storage Expense | To use solar energy at night or during low sunlight, battery storage is needed, which can be expensive and significantly increase the system cost. |
| Space Requirements | Solar panels require adequate roof or ground space, which can be limited for some properties, and installation on shaded, flat, or north-facing roofs reduces efficiency. |
| Roof Suitability & Structural | Not all roofs are suitable due to orientation, shading, or structural limitations (solar panels can weigh over 300 kg), requiring evaluation before installation. |
| Efficiency Degradation Over Time | Solar panels’ energy output declines gradually over the years (about 0.4% degradation per year), reducing efficiency after 20-25 years. |
| Limited Recycling Options | At the end of life, recycling solar panels remains limited, though improvements are expected in the future. |
| Environmental Impact of Production | Manufacturing and transporting panels involve pollution and resource use, though operational solar power is clean. |
The biggest risk of solar panels
The biggest risk of solar panels in 2025 involves a combination of intensified extreme weather impacts and operational challenges that affect their performance, safety, and financial viability.
Key risks include:
- Extreme Weather Damage:
- Severe weather events such as hailstorms, strong winds, heavy rain, and thermal stresses due to daily temperature fluctuations pose significant risks of physical damage to solar panels. Hail, in particular, is noted as one of the most severe financial risks if the panels are not properly protected with thicker glass or appropriate mounting techniques.
- Performance Under Climate Change: Climate change introduces uncertainty and extreme meteorological variations that can reduce solar panel energy output over time. One case study estimated about 4.9% power loss over 30 years due to increased extreme weather despite potentially more sunny days.
- Maintenance and Operational Risks: Issues like dust and dirt accumulation, shading from new obstructions, electrical wiring problems, and aging or failure of components (e.g., inverters and batteries) can reduce efficiency and increase costs.
- Cybersecurity Threats: With solar and battery energy storage systems increasingly integrated into the grid, cybersecurity risks are rising, necessitating enhanced protection.
- Fire Risks and Safety: Poor planning or design can increase fire risk, which damages not only the solar system but also the property it is installed.
Overall, physical damage from extreme weather combined with operational and cybersecurity risks form the biggest challenges for solar panels in 2025. Proper system design, protective technologies, regular maintenance, and cybersecurity measures are essential to mitigate these risks.
Safety risks for neighbours
Solar panels are also a great source of clean energy. According to Columbia University, solar panels lower carbon emissions per acre than trees! Solar panels also reduce reliance on fossil fuels and help you live more sustainably. With solar, you can go green and keep the green in your wallet — sounds worth it to us!
Contrary to common solar myths about harmful chemicals, the materials used to make solar panels are sealed and contained, so they do not negatively affect the surrounding area. Solar panels contain a variety of materials, including silicon and different types of metals.
This could interfere with small devices like shortwave radios, but solar panels do not give off radiation to the extent that it is dangerous to humans. Additionally, this minimal level of radiation will be emitted away from your house, either off the top of your roof or out from wherever your panels are located.
Risk of cancer:
No, there is no scientific research linking solar panels to cancer. There is no scientifically established connection between non-ionizing electromagnetic frequencies (EM fields) and cancer. The levels of electromagnetic frequencies given off by solar panels are so weak that they are probably not even reaching you if your panels are on a roof or a ground-mounted system any distance away from your home.
There are scientific studies that have shown a correlation between long-term exposure to stronger EMF radiation outputs and cancer. But even then, there is no concrete proof that high levels of regular exposure to EMF radiation cause cancer.
Scientists can say that living within 600 meters of high voltage power lines could increase the chances of cancer development, especially in children, but it is not all children or people. And those studies were of the effects of high-voltage power lines, not solar panels.
The risk of Solar energy
Solar energy is intermittent because it relies on sunlight, which is not available 24/7 due to the Earth’s rotation and weather conditions. This means solar power generation is limited to daylight hours and can be significantly reduced by cloud cover, rain, or other weather phenomena. While advancements like battery storage help mitigate this, it remains a key challenge for the widespread adoption of solar energy.
Here’s a more detailed look:
- Day/Night Cycle:
The most obvious limitation is that solar panels only generate electricity when exposed to sunlight. This means they cannot produce power at night, requiring alternative energy sources or storage solutions. - Weather Conditions:
Cloud cover, rain, snow, and even smog can significantly reduce the amount of sunlight reaching solar panels, impacting their output. - Seasonal Variations:
Solar energy generation also varies with the seasons, with lower output during winter months in many parts of the world due to shorter daylight hours and increased cloud cover. - Location:
The amount of solar radiation varies by location. Some areas receive more sunlight than others, making solar energy a more cost-effective option in those regions, according to PVcase. - Technological Limitations:
While advancements in battery storage and solar panel efficiency are ongoing, they still face limitations in terms of cost, capacity, and lifespan, according to a Quora post.
Famous PV case
PVcase is an end-to-end solar project development platform for site selection, PV design, and yield optimization, offering an alternative to manual methods and delivering optimal results in significantly less time. Whether you use a single product or the entire platform, PVcase accelerates project timelines and reduces costs at every stage of solar project development.
Trusted by over 1,500 customers in 75+ countries, including industry leaders like AES, ib Vogt, RWE, Voltalia, and Iberdrola, we underpin the development of more than 4 TW projects annually.
Risk of Performance and Efficiency

risk of performance in cloudy days
Rooftop solar’s performance isn’t as constant as its sun-powered reputation suggests. Cloudy days, seasonal variations, and even dust buildup can significantly impact energy production. This means your solar factory might not always churn out enough electricity to meet your needs, especially during peak demand.
Maintenance challenges associated with solar panel systems
The maintenance of solar panels includes the following:
- Dust, Dirt, and Debris Accumulation
Solar panels can get covered by dust, pollen, leaves, bird droppings, and other debris, which block sunlight and reduce energy output by up to 25%. Regular cleaning is essential, especially in dusty areas or places with frequent bird activity.
- Weather-Related Degradation
Thermal cycling caused by temperature fluctuations (daily heating and cooling) stresses the materials in panels, potentially causing microscopic cracks and degrading electrical connections over time. Moisture and humidity, especially in coastal or wet regions, can cause internal corrosion by penetrating tiny cracks or poorly sealed parts. Extreme weather like hail, heavy rain, and strong winds can physically damage panels or mounts.
- Electrical and Mechanical Issues
Loose wiring, terminals, or connections can reduce system efficiency and may cause power losses or failures. Wires can be pinched or damaged by rodents or environmental factors. Inverters, a critical component, usually need replacement every 10-15 years, adding to maintenance costs. Monitoring systems also require calibration and updates.
- Shading and Physical Obstructions
Growing trees, new buildings, or accumulated debris can cause shading, which significantly lowers solar panel efficiency. Continuous monitoring and trimming or relocating obstructions is necessary.
- Cleaning and Inspection Logistics
Cleaning must be done carefully with non-abrasive tools and ideally during cooler parts of the day to prevent streaks or damage. Professional inspections are recommended at least annually to catch issues early. For large arrays or challenging locations (roofs, complex terrain), maintenance can be logistically difficult and may require specialized equipment and trained personnel.
- Structural and Weatherproofing Concerns
The mounting structures and seals need periodic inspection for corrosion, wear, and weather resistance to prevent damage and maintain system integrity.
So, to maintain solar panel systems optimally, owners must invest in regular cleaning, timely inspections, monitoring electrical connections, and addressing environmental challenges like weather and shading.
Professional servicing is often needed, especially for complex or large installations, to prevent efficiency losses and costly repairs.
These maintenance challenges are common industry-wide and crucial to consider for long-term solar panel performance and durability.
Safety for humans and animals
Solar panels are designed to be safe for you and the animal world. Solar panels are low voltage and are encapsulated with electrical insulation. Any solar system that is installed correctly is grounded to prevent any danger of electrocuting someone from touching the solar system. Just like any other electrical device.
Shadows on Equity and Accessibility
The upfront costs and complex installation requirements of rooftop solar power can create an uneven playing field. Wealthier homeowners and businesses are more likely to benefit from this technology, leaving lower-income communities behind in the quest for clean energy.
Rooftop solar power still holds immense promise for a brighter, more sustainable future. However, it’s crucial to approach it with open eyes and consider all its facets.
Weigh the financial costs, assess your roof’s suitability, and explore alternative renewable energy options that might better fit your needs and budget.
Remember, responsible energy choices demand a nuanced understanding of both the sunshine and the shadows.
Conclusion:
Rooftop solar power has a dark side, but it is a powerful tool in the fight against climate change, but it’s not a one-size-fits-all solution.
Recognizing its limitations and potential downsides allows us to make informed choices, advocate for equitable access, and ensure that our pursuit of sun-powered energy shines even brighter on the path to a sustainable future.
Also Read: https://solaratics.com/selling-home-in-usa-with-solar-panels/
Momentum Solar Pyramid Scheme, COST, FACTS (Updated 2025)
Frequently Asked Questions:
Consider your budget, roof suitability, and energy needs. Consult with solar experts and compare options before making a decision.
The manufacturing and disposal of panels present challenges, but advancements in technology are improving their sustainability.
Explore options like wind power, geothermal energy, and community solar programs to find the best fit for your needs and environment.
